用PCA主成分分析法理解代谢组混合物
Understanding Metabonomics Mixtures with PCA
Abstract
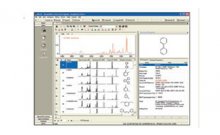
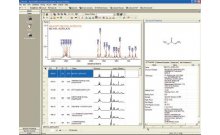
In toxicology studies, alterations to the intrinsic in vivo biochemical profile of an animal can be monitored via NMR spectroscopic analysis of urine. Chemometric processing of the NMR data can enhance understanding of the toxic effects; in particular, examination of the principal component analysis (PCA) scores provides insight into these data in a time-efficient manner.
Conclusions
Combining the capabilities of a database with principal component analysis gives the analyst the capability of evaluating trends in NMR quickly and efficiently. The PCA work leads directly to the identification of key profiles, simplifying the effort of sifting through hundreds or even thousands of spectra. In addition, this analytical approach is an efficient means of identifying underlying biochemical events (control, toxicity, time-related change, etc.). The study of toxins or drugs in development can benefit substantially.