用NMR和多变量分析进行糖尿病诊断
Toward Diagnosis of Diabetes by NMR and Multivariate Analysis
Abstract
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is becoming a key tool for understanding the metabolic processes in living
systems. Among its many applications, advanced spectroscopic techniques are combined with multivariate statistical approaches to provide diagnostic information for diseases and to identify the changes in the metabolic pathways [1,2]. This study demonstrates the potentials of this approach by the multivariate analysis of the 1 H NMR spectra of serum samples from diabetic and healthy people.
Conclusions
This technical note demonstrates the potentials of applying MR-based metabolomics in disease diagnostics and in order o identify the changes of metabolic pathways. While further laboration can be made in the analyses from this initial study in the future and continued improvements will be made in future generations of the software, the following conclusions can be currently drawn:
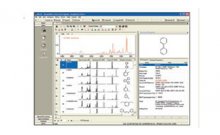
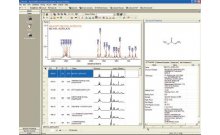
1. The macro-based batch processing of metabolomics NMR spectra using KnowItAll ® ProcessIt™ NMR and MineIt™ significantly improves the efficiency of spectral processing and management, which is usually both tedious and time consuming.
2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of the metabolomics NMR data of the serum samples using KnowItAll ® Informatics System's AnalyzeIt™ MVP application provides a reliable way to diagnose diabetes.
3. The traditional PCA loadings plots and the novel OD heatmap profiles generated using the KnowItAll ® platform provide different approaches to identifying the differences between the spectra, which opens the door to further identifying key metabolites or biomarkers.
4. Searching a spectral library of common metabolites provides a helpful method for identifying changed metabolites.
5. When spectral misalignment is not serious, it is preferable to run the PCA analysis of the metabolomics NMR data at the datapoint resolution, rather than using the traditional binning and bucketing.