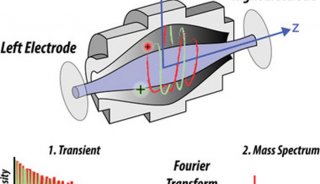
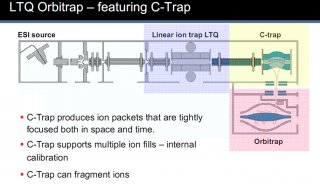
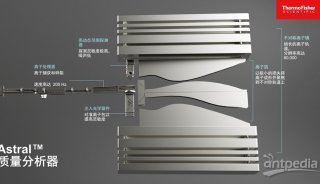
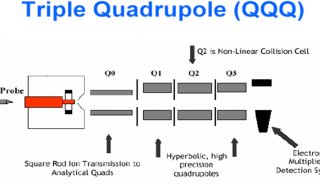
2010全国质谱大会大会报告(三)
来自诺华(Novartis)制药的Wang, Karen(王瑛琪)教授,做了题为“Application of Mass Spectrometry in Pharmaceutical Drug Discovery Research”(新药发现研究中质谱的应用)的报告。质谱法已被广泛应用于药物研发,从支持传统的药物化学(合成),到药物代谢和药代动力学研究。日前制药产业面临更严格的挑战来研发治疗疾病的途径和靶标,从目标物发现到生物标志物鉴定都需要创新的方法。同时,这些挑战也给了科学家在创新领域的巨大机会,这些创新很多来源于跨学科(化学、生物、技术)的努力。王教授介绍了在药物研发领域的四种创新方法。(1)通过代谢组和蛋白质组分析来进行目标物鉴定和验证;(2)使用基于质谱的筛选方法来进行发现研究和验证;(3)治疗性单克隆抗体的药动分析,(4)药物组织分布的质谱成像分析。以下是英文摘要:
Mass spectrometry has been extensively utilized in drug discovery research and development, from the traditional medicinal chemistry support to drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic studies. As the industry faces with the challenges of tougher diseases and more challenging pathways/targets to tackle, it requires the development of innovative solutions to address needs from target discovery to biomarker identification. It also presents a great opportunity for scientists in the field for innovation, many of which often come from cross disciplinary efforts-chemistry, biology and technology. In this presentation, four areas of drug discovery research where innovative solutions have been developed will be presented (1)target identification and validation through cellular metabolomic analysis and chemical proteomics; (2)hits discovery research and validation using MS-based screening; (3)PK analysis of therapeutic monoclonal antibody; (4)MS imaging for drug tissue distribution, Investment in life saving and life style improving medicines will get more intensified as standard of living improves. Drug discovery research will continue to require and present opportunity for such application driven innovations.
台湾中央研究院化学研究所 Yu-Ju Chen(陳玉如)教授
来自台湾中央研究院化学研究所的Yu-Ju Chen(陳玉如)教授,做了题为“Integrated Membrane Proteomic Strategies Revealed Cell Surface Signature during Human Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation”(在人类胚胎干细胞分化中用集成的膜蛋白质组策略揭示细胞表面签名)的报告。在干细胞研究中,细胞表面的标志物被广泛用于干细胞的分类,监测分化阶段以及在再生医学的使用净化。膜蛋白质组的定量方法将使科学家能深入观察干细胞分化阶段、世系特异性表达,可增加对同类的主要干细胞群的理解。然而,膜蛋白质组非常多样的糖基化使其分析实验充满挑战,因为它们的疏水性和低丰度,这严重影响其溶解性、样品处理分离和质谱分析。陈教授课题组发展了一种蛋白质组学和糖基化蛋白质组轮廓方法,用于人类胚胎干细胞和16天后分化的胚状体生长物的“膜蛋白质组轮廓”测定,结果显示,在多种细胞途径中,差别表达的糖蛋白和膜蛋白图和许多过程有关,包括细胞分化、细胞增殖、细胞发育,说明在干细胞分化中,不仅是蛋白标志物,而且糖基化的位点和程度在复杂的过程中都具有显著可区分的模式(pattern)和功能。以下是英文摘要:
In stem cell research, cell surface markers are extensively used for stem cell classification, monitoring the differentiation stages as well as purification for their use in regenerative medicine. Quantitative membrane proteomic approaches will provide an in-depth view of the stage and lineage-specific expression which potentially enhances our understanding on the homogeneous primary stem cell population. However, the analysis of membrane proteome and its highly heterogeneous glycosylation is experimentally challenging because of their hydrophobic nature and low abundance, which seriously complicate their solubilization, sample handling separation, and mass spectrometric analysis.
In attempt to search for novel stem cell surface makers and differentiation regulators, we have applied a subglobal proteomic approach and glycoproteomic profiling to define a “membrane proteomic profile” of human embryonic stem(hES) cell and 16-day differentiated embryoid body (EB) outgrowth. Using our recently reported gel-assisted digestion and iTraq labeling approach, 3842 proteins were identified (p<0.05) and 2783 proteins were quantified with >=2peptide. By labeling strategy with alkynyl sugar derivatives, the preliminary results In glycoproteomic analysis identified 350 glycopeptides (p<0.05) and quantified in 212 glycoproteins. By combining the quantitative information in protein expression and N-glycosylated peptides, the site-specific glycosylation degree of peptides can be confidently determined on a proteome scale. Our study revealed the dramatic change in expression as well as sialylated N-glycosylation on cell surface glycoproteome during stem cell differentiation. Interestingly, the proteomic data revealed that some cell surface makers, previously discovered by gene expression array, have unaltered expression during stem cell differentiation, which may be due to differences in protein turnover and regulation of the abundance of cellular mRNA and proteins. Mapping of these differentially expressed glycoproteins and membrane proteins in multiple cellular pathways related to cell differentiation, proliferation and cell development suggests that not only the protein makers but also the site and degree of glycosylation have distinct pattern or function in the complex process during stem cell differentiation.
中国医学科学院药物所 再帕尔•阿不力孜教授
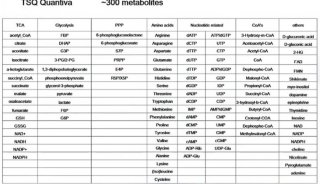
中国医学科学院药物所的再帕尔•阿不力孜教授做了题为“基于RRLC-MS/MS 的代谢组学高通量分析方法研究:恶性肿瘤的生物标志物的发现”的报告。再帕尔教授介绍,目前代谢组学的分析手段主要有NMR和MS两种。NMR无需复杂的前处理、无损,鉴定能力强,检测无歧视,但存在灵敏度低,不能准确定量的缺点;MS具有高灵敏度、准确定量、靶分析的优势,也存在离子化歧视,结构鉴定能力较弱的缺陷。
再帕尔教授提出了一种基于RRLC-MS/MS的高通量代谢组学方法,通过混合标准溶液的LC-MS分析来分析系统的稳定性控制,用QC样本的LC-MS分析来进行数据的可靠性验证。并列举的乳腺癌和宫颈癌的的标志物分析实例。最后,再帕尔教授指出,用LC-MS来研究代谢组学,必须结合ESI、APCI多种离子源,才能尽可能完整地发现生物标志物。