乳腺癌化疗后癌细胞可转化为癌症干细胞引起耐药
2017年2月21日,美国《细胞》旗下《细胞·报告》正式发表约翰·霍普金斯大学的研究报告,发现乳腺癌化疗后癌细胞可转化为癌症干细胞引起耐药。
对于许多患者而言,化疗获益短暂,化疗后的乳腺癌复发常常致命,乳腺癌干细胞对化疗有很强的耐药性,对治疗构成严重问题。既往研究表明,对化疗耐药的乳腺癌,往往由于癌症干细胞的顽固特性引起,这种干细胞通常存在于氧气水平较低的肿瘤中心,通过缺氧诱导因子(HIF)生存,其启动帮助细胞在低氧环境中存活的基因。
该研究分析了多种人类乳腺癌细胞株接触化疗药物的情况,例如通过破坏癌细胞DNA而阻止肿瘤生长的卡铂。结果发现,存活的癌细胞往往具有较高水平的谷胱甘肽S-转移酶Ω1(GSTO1)。实验表明,当乳腺癌细胞接触化疗药物时,HIF控制GSTO1的产生;如果在这些实验室培养的细胞中阻断HIF活性,则不产生GSTO1。GSTO1及其相关GST蛋白是抗氧化酶,但是GSTO1在化疗耐药中的作用不需要其抗氧化活性。相反,在化疗后,GSTO1与兰诺定受体RYR1结合,触发钙的释放,引起将普通乳腺癌细胞转化为癌症干细胞的连锁反应。
为了更直接地评估GSTO1和RYR1在乳腺癌对化疗耐药中的作用,该研究将人乳腺癌细胞注入小鼠乳腺,然后在肿瘤形成后用卡铂治疗。除了使用普通的乳腺癌细胞,还使用GSTO1或RYR1表达部分丧失或降低的癌细胞。结果发现GSTO1或RYR1表达部分丧失或降低可使原发肿瘤的癌症干细胞数量减少,并可阻止癌细胞从原发肿瘤转移到肺部。
因此,研究表明通过抑制HIF继而阻断GSTO1表达,可能提高化疗药物如卡铂的效果,研究者正在努力开发可以抑制HIF作用的药物,希望HIF抑制剂将使化疗更有效。
Cell Rep. 2017 Feb 21;18(8):1946-1957.
Chemotherapy-induced Ca2+ release stimulates breast cancer stem cell enrichment.
Lu H, Chen I, Shimoda LA, Park Y, Zhang C, Tran L, Zhang H, Semenza GL.
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21205, USA.
Highlights
Exposure of breast cancer cells to carboplatin induces HIF-dependent GSTO1 expression
GSTO1 interacts with ryanodine receptor 1 to increase intracellular Ca2+ levels
Ca2+ triggers PYK2 → SRC → STAT3 signaling, leading to breast cancer stem cell enrichment
GSTO1 knockdown blocks cancer stem cell enrichment, tumor initiation, and metastasis
Breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs) play a critical role in tumor recurrence and metastasis. Exposure of breast cancer cells to chemotherapy leads to an enrichment of BCSCs. Here, we find that chemotherapy induces the expression of glutathione S-transferase omega 1 (GSTO1), which is dependent on hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2. Knockdown of GSTO1 expression abrogates carboplatin-induced BCSC enrichment, decreases tumor initiation and metastatic capacity, and delays tumor recurrence after chemotherapy. GSTO1 interacts with the ryanodine receptor RYR1 and promotes calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum. Increased cytosolic calcium levels activate PYK2 → SRC → STAT3 signaling, leading to increased expression of pluripotency factors and BCSC enrichment. HIF inhibition blocks chemotherapy-induced GSTO1 expression and BCSC enrichment. Combining HIF inhibitors with chemotherapy may improve clinical outcome in breast cancer.
KEYWORDS: breast cancer stem cell; chemotherapy; hypoxia-inducible factors; metastasis; pluripotency factors; tumor initiation; tumor recurrence
PMID: 28228260
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.001
-
项目成果
-
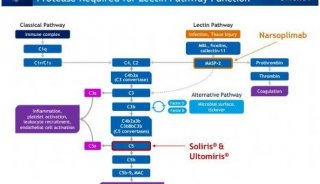
焦点事件
-
项目成果