首次对广泛耐药分枝杆菌进行苏基尼-普氏分析
Xie L., et al. (2015) First Succinyl-Proteome Profiling of Extensively Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium
Abstract:
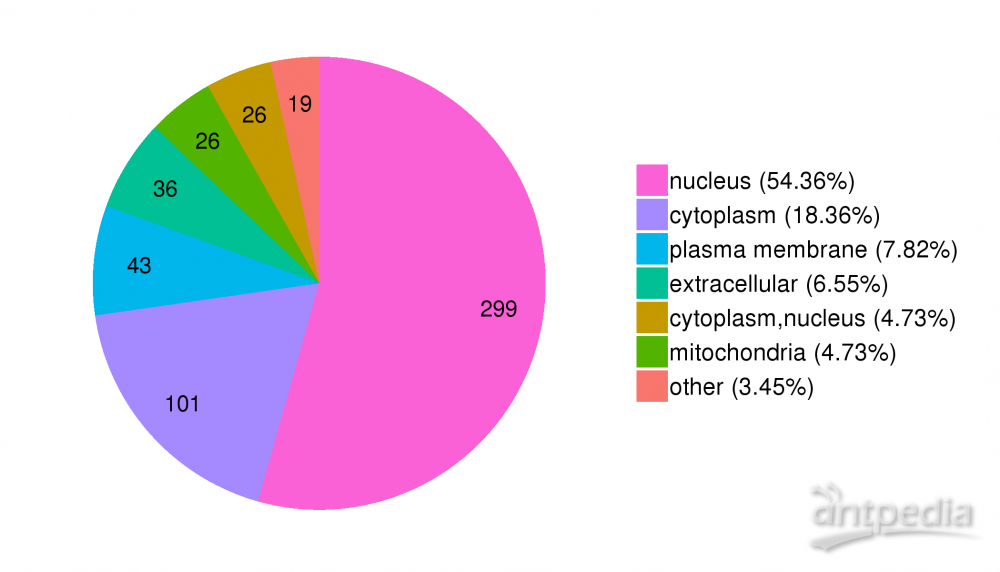
Protein lysine succinylation, an emerging protein post-translational modification widespread among eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, represents an important regulator of cellular processes. However, the extent and function of lysine succinylation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, especially extensively drug-resistant strain, remain elusive. Combining protein/peptide prefractionation, immunoaffinity enrichment, and LC-MS/MS analysis, a total of 686 succinylated proteins and 1739 succinylation sites of M. tuberculosis were identified, representing the first global profiling of M. tuberculosis lysine succinylation. The identified succinylated proteins are involved in a variety of cellular functions such as metabolic processes, transcription, translation, and stress responses and exhibit different subcellular localization via GO, protein interaction network, and other bioinformatic analysis. Notably, proteins involved in protein biosynthesis and carbon metabolism are preferred targets of lysine succinylation. Moreover, two prevalent sequence patterns: EK(suc) and K*****K(suc), can be found around the succinylation sites. There are 109 lysine-succinylated homologues in E. coli, suggesting highly conserved succinylated proteins. Succinylation was found to occur at the active sites predicted by Prosite signature including Rv0946c, indicating that lysine succinylation may affect their activities. There is extensive overlapping between acetylation sites and succinylation sites in M. tuberculosis. Many M. tuberculosis metabolic enzymes and antibiotic resistance proteins were succinylated. This study provides a basis for further characterization of the pathophysiological role of lysine succinylation in M. tuberculosis.
摘要:
蛋白溶酶化是一种在真核细胞和原核细胞中广泛传播的新兴蛋白质转化后修饰,是细胞过程的重要调节器。然而,在结核分枝杆菌中,特别是广泛的耐药菌株中,利辛酸的消融程度和作用仍然难以捉摸。结合蛋白质/肽介量、免疫亲和力浓缩和LC-MS/MS分析,共鉴定了686个琥珀化蛋白和1739个M.结核病的琥珀化位点,代表了全球首次对M.结核病裂化酶进行分析。所识别的杀菌蛋白涉及各种细胞功能,如代谢过程、转录、翻译和压力反应,并通过GO、蛋白质相互作用网络和其他生物信息分析表现出不同的亚细胞定位。值得注意的是,蛋白质生物合成和碳代谢中涉及的蛋白质是莱辛琥珀化的首选靶点。此外,在琥珀化位点周围可以找到两种流行的序列模式:EK(suc)和K_K(suc)。大肠杆菌中有109种莱辛-琥珀酸的共乳糖,表明这种蛋白质保存性高。在Prosite签名(包括Rv0946c)预测的活跃地点,发现苏奇尼辛发生,表明裂温的琥珀化可能会影响他们的活动。在M.结核病的乙酰化位点和琥珀化位点之间存在着广泛的重叠。许多M.结核病代谢酶和抗生素耐药性蛋白被琥珀化。本研究为进一步表征利子在M.结核病中的病理生理作用提供了依据。