| ABSTRACT |
|
The expression of foreign proteins at high levels in E. coli often results in the formation of inclusion bodies composed of insoluble aggregates of the expressed protein. The inclusion bodies are recovered from bacterial lysates by centrifugation and are washed with Triton X-100 and EDTA to remove as much bacterial protein as possible from the aggregated foreign protein.
To obtain soluble protein, the washed inclusion bodies are dissolved in denaturing agents and the released protein is then refolded by gradual removal of the denaturing reagents by dilution or dialysis. Whereas the procedure given here has been used to solubilize inclusion bodies, each protein may require a slightly different procedure, which must be determined empirically. |
|
|
|
| MATERIALS |
|
| Reagents and Solutions |
|
Cell lysis buffer I 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 8.0) 1 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) 100 mM NaCl Cell lysis buffer II 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 8.0) 10 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) 100 mM NaCl 0.5% (v/v) Triton X-100 Deoxycholic acid, protein grade HCl (12 M) (concentrated HCl) Inclusion body solubilization buffer I (prepare just before use) 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 8.0) 1 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) 100 mM NaCl 8 M urea 0.1 M PMSF or Pefabloc SC Inclusion body solubilization buffer II 50 mM KH2PO4 (pH 10.7) 1 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) 50 mM NaCl KOH (10 N) PMSF (phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride)(17.4 mg/ml in isopropanol at -20°C)
An alternative to PMSF, Pefabloc SC, is nontoxic and stable in buffered aqueous solutions. Tris-Cl (0.1 M, pH 8.5) with urea.
For use in Method 2 of Step 7. Prepare 0.1 M Tris-Cl (pH 8.5) with increasing concentrations of urea (e.g., 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 M). Because urea decomposes in aqueous solutions, make the solution fresh from solid urea and use immediately.
|
|
| Vectors and Hosts |
|
|
|
| Enzymes and Buffers |
|
Gels/Loading Buffers10% Polyacrylamide gel containing SDS 1x SDS gel-loading buffer 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 6.8) 2% (w/v) SDS, electrophoresis grade 0.1% (w/v) bromophenol blue
Add dithiothreitol from a 1 M stock to a final concentration of 100 mM just before the buffer is used in Step 13.
2x SDS gel-loading buffer 100 mM Tris-Cl (pH 6.8) 4% (w/v) SDS, electrophoresis grade 0.2% (w/v) bromophenol blue 20% glycerol
Add dithiothreitol from a 1 M stock to a final concentration of 100 mM just before the buffer is used in Steps 7 and 14.
|
|
| Centrifuges/Rotors/Tubes |
|
Additional ItemsGlass rod (polished) pH paper
|
|
|
|
METHOD
|
|
Centrifuge 1 liter of the cell culture of E. coli expressing the protein of interest at 5000g (5500 rpm in a Sorvall SLC-1500 rotor) for 15 minutes at 4°C in preweighed centrifuge bottles.
IMPORTANT: Perform Steps 2-4 at 4°C.
Remove the supernatant and determine the weight of the E. coli pellet. For each gram (wet weight) of E. coli, add 3 ml of cell lysis buffer I. Resuspend the pellet by gentle vortexing or by stirring with a polished glass rod.
For each gram of E. coli, add 4 µl of 100 mM PMSF or Pefabloc SC and then 80 µl of 10 mg/ml lysozyme. Stir the suspension for 20 minutes.
Stirring continuously, add 4 mg of deoxycholic acid per gram of E. coli.
Store the suspension at 37°C and stir it occasionally with a glass rod. When the lysate becomes viscous, add 20 µl of 1 mg/ml DNase I per gram of E. coli.
Store the lysate at room temperature until it is no longer viscous (~30 minutes).
Purify and wash the inclusion bodies using one of the following two methods.
Method 1: Recover inclusion bodies using Triton X-100
Method 2: Recover inclusion bodies using urea
Centrifuge the cell lysate at maximum speed for 15 minutes at 4°C in a microfuge.
IMPORTANT: Perform Steps b, d, and f at 4°C.
The following steps involve washing and solubilization of inclusion bodies with buffers containing different concentrations of urea.
Decant the supernatant. Resuspend the pellet in 1 ml of H2O per gram of E. coli. Transfer 100-µl aliquots to four microfuge tubes and store the remainder of the suspension at 4°C.
Centrifuge the 100-µl aliquots at maximum speed for 15 minutes at 4°C in a microfuge.
Discard the supernatants. Resuspend each pellet in 100 µl of 0.1 M Tris-Cl (pH 8.5) containing a different concentration of urea (e.g., 0.5, 1, 2, and 5 M).
Centrifuge the tubes at maximum speed for 15 minutes at 4°C in a microfuge.
Decant the supernatants and set them aside for the next step. Resuspend each pellet in 100 µl of H2O.
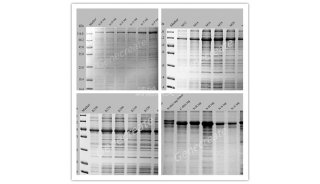
Remove 10-µl samples of each supernatant and each resuspended pellet. Mix each sample and resuspended pellet with 10 µl of 2x SDS gel-loading buffer and analyze by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to determine which concentration of urea yields the best recovery of the inclusion bodies.
Use the appropriate concentration of urea, determined in Step g, to wash the remaining pellet (from Step b) as described in this method.
If necessary, proceed with Step 8 to solubilize the inclusion bodies.
Centrifuge the cell lysate at maximum speed for 15 minutes at 4°C in a microfuge.
Decant the supernatant. Resuspend the pellet in 9 volumes of cell lysis buffer II at 4°C.
Store the suspension for 5 minutes at room temperature.
Centrifuge the tube at maximum speed for 15 minutes at 4°C in a microfuge.
Decant the supernatant and set it aside for the next step. Resuspend the pellet in 100 µl of H2O.
Remove 10-µl samples of the supernatant and of the resuspended pellet. Mix each sample with 10 µl of 2x SDS gel-loading buffer and analyze the samples by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to determine which fraction contains the protein of interest.
If necessary, proceed with Step 8 to solubilize the inclusion bodies.
Centrifuge the appropriate resuspended pellets from Step 7 at maximum speed for 15 minutes at 4°C in a microfuge and suspend them in 100 µl of inclusion-body solubilization buffer I containing 0.1 mM PMSF or Pefabloc SC (freshly added).
Store the solution for 1 hour at room temperature.
Add this solution to 9 volumes of inclusion-body solubilization buffer II and incubate the mixture for 30 minutes at room temperature. Check that the pH is maintained at 10.7 by spotting small aliquots onto pH paper. If necessary, readjust the pH to 10.7 with 10 N KOH.
Adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0 with 12 M HCl and store the adjusted solution for at least 30 minutes at room temperature.
Centrifuge the solution at maximum speed for 15 minutes at room temperature in a microfuge.
Decant the supernatant and set it aside for the next step. Resuspend the pellet in 100 µl of 1x SDS gel-loading buffer.
Remove 10-µl samples of the supernatant and resuspended pellet. Mix the supernatant sample with 10 µl of 2x SDS gel-loading buffer. Analyze both samples by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to determine the degree of solubilization.
|
|
|
|
Anyone using the procedures in this protocol does so at their own risk. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory makes no representations or warranties with respect to the material set forth in this protocol and has no liability in connection with the use of these materials. Materials used in this protocol may be considered hazardous and should be used with caution. For a full listing of cautions regarding these material, please consult:
Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual Third Edition, by Joseph Sambrook and David W. Russell, © 2001 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, p. 15.49. |
|
| Copyright © 2006 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. All rights reserved. No part of these pages, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than personal use. Therefore, reproduction modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission. |