血浆中芬太尼的检测
芬太尼是60 年代研制合成的阿片类药物,主要用于麻醉,现已成为全球麻醉药品增长最快的品种。在我国麻醉药品中的市场份额亦逐步提高,市场销售量在国内现有麻醉药品中居第2位,已成为我国使用最多的麻醉药品之一。近年来,国内外多应用灵敏、快速、高自动化的分析仪器实现对血浆中低浓度芬太尼的检测,以满足药物动力学研究以及司法鉴定的要求。
1检测方法
1.1萃取方法
近10年国内外检测血浆中芬太尼,前处理过程中血浆除杂质多用氢氧化钠或氢氧化钾碱化分离沉淀得以实现,而萃取过程却不尽相同。下面主要对萃取方法及相应回收率作一简单的对比和分析。
1.1.1固相萃取法(SPE)
国内外应用SPE 法进行前处理的报道较少,Weng Naidong等分别用Bond Elut Certify(mixed2mode)、Oasis HLB及C18为萃取柱对人血浆中的芬太尼及可乐宁等其它药物进行提取并比较,3种固相萃取柱的回收率分别为81% ,73% ,32%[1];James j.Kuhlman 等使用Varian BondElut L RC2Certify columns为萃取柱提取血浆中的芬太尼,回收率为88 %[2]。
固相萃取操作简单, 处理样品速度快, 不会象液-液萃取可能出现分离不完全甚至出现乳化、回收率较低等现象,而且不会产生大量的有机废液;但缺点是固相萃取柱价格较高,且毒物的种类不同需要选择不同的固相材料,且洗脱条件(包括洗脱所用溶剂,洗脱时间等) 都要因分离对象不同而进行实验筛选,才能满足尽量高的回收率及尽量减免杂质干扰,正是这些原因,使SPE 法的应用受到了一定的限制。
1.1.2液-液萃取(LLE)
液-液萃取法是应用广泛的提取血浆中芬太尼的方法,萃取剂的选择也多种多样。国内报道多应用正己烷∶乙醇(20∶1,v/v) 为萃取剂,如张燕婉等及李正翔等均用正己烷∶乙醇(20∶1,v/v) 为萃取剂提取人血浆中的芬太尼,检测不同浓度的提取回收率分别在85.29~89.34%,88.0~89.6%(2次萃取)之间[3、4]。李正翔等还曾试用正己烷 -异丙醇、正丁醇 -异丙醇、正己烷 -乙醚等,效果均不如正己烷 -乙醇理想。
国外应用的萃取剂种类较多,提取回收率亦各不相同,其中应用单一萃取剂对血浆中的芬太尼进行提取的回收率如表1所示[6~11]。
另外,国外也有先用一种萃取剂提取芬太尼,再应用另一种溶剂进行反萃取的报道。K.Kumar等用庚烷∶异戊醇(98∶2,v/v)萃取,0.5mol/L,pH = 2.8(磷酸调节) 的磷酸二氢钾溶液反萃取,回收率为82.5±5.1%[5];Liu Yuangsheng等先用环己烷∶异戊醇(197∶3) 萃取,然后用0.125mol/L硫酸反萃取,
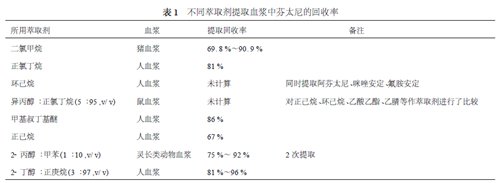
经碱化后再用正己烷萃取的方法提取人血浆中的芬太尼,3种不同血药浓度的回收率分别为99.0±5.5%,99.6±4.3%,100.1±2.7%[12]。可见,应用反萃取的方法可获得较高的提取回收率,且精密度较好。但操作步骤相对复杂,所需时间长,产生废液多。
综上所述,多种萃取剂都能实现对芬太尼的有效提取并取得大于65%的提取回收率。在不要求准确定量的情况下,可选用相对毒性较低、易挥发、提取过程操作时间短的萃取剂进行一步提取,便可满足定性分析芬太尼的需要。
1.2检测分析方法
1.2.1分光光度法( spect rop hotomet ric)
紫外-可见分光光度法在芬太尼的检测中应用较广。Yan-nis Dotsikas等用紫外2可见分光光度法检测产妇与婴儿血浆中的芬太尼并与化学发光酶免疫测定法比较,最低检测血药浓度为0.045 ng/ml[13]。因血浆检材中可能含有紫外吸收的杂质,干扰芬太尼的测定,使得本方法单独应用受到一定的限制;另外,随近年来气质联用仪及液质联用仪的广泛应用,该方法已逐渐不再被应用。
1.2.2免疫分析法(immunoassay,IA)
Bronwyn Fryirsa 等用放射性免疫测定方法测定人血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.2ng/ml[7];H.Kafer-stein与G.Sticht应用非放射性微量滴定板酶免疫测定法检测人血清中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.5ng/ml[14];另外,2000年T.D.Egan等[15]、C.R.Valverde 等[16]、D.D.Lee 等[17] 均用放射性免疫测定法检测血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.1ng/ml; Yannis Dot sikas 等用化学发光酶免疫测定法检测产妇与婴儿血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度达0.0048ng/ml[13]。
免疫分析法具有灵敏度高、选择性强、操作简便、检测省时及耗材少等优点。但应用免疫分析法检测血浆芬太尼需要的专用试剂具有一定的时效性,而且实验重复性、选择性较差,检测结果大多需要验证,使该法的推广、运用受到一定的限制。
1.2.3气相色谱法(GC)
R.J.H. Woestenborghs等[18]与S.R.Kowal ski等[19]分别用GC-TSD和GC-NPD 方法检测人血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度均为0.25ng/mlLiu Yuansheng等用GC2NPD方法检测人血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.2ng/ml[12];Hak Soo Choi等用GC-NPD方法检测鼠血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度达0.1ng/ml[9]。
1.2.4高效液相色谱法(HPLC)
M.Tsuchiya 等用HPLC方法检测人血浆中芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.158ng/ml[20];张燕婉等[3]、李正翔等[4]均用HPLC-UV方法检测人血浆中芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度均为5ng/ml;K. Kumar 等[5]、E.J.G.Portier等[8]亦用HPLC2UV 法检测人血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度分别为2ng/ml ,0.2ng/ml。
1.2.5气相色谱/ 质谱联用(GC/MS)
气相色谱与质谱的联用,已成为一种极强有力的、可以分离和鉴定复杂混合物组成及结构的可靠手段。AndrasSzeitz等用GC/MS法检测猪血清中芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.05ng/ml[6] ;Bronwyn Fryisa 等用GC/MS法检测人血浆中芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.020ng/ml[7];2003年Jamesj.Kuhlman,Jr等用GC/MS法检测人血浆、胆汁、肝,尿及其它检材中的芬太尼,其中血浆中芬太尼的最低检测血药浓度为1ng/ml[2]。
GC/MS方法是分析和确证检材中微量或痕量毒物的有力工具,在很大程度上弥补了普通气相色谱法的不足和缺陷,其检测灵敏度也高于HPLC法。
1.2.6液相色谱-质谱联用(LC-MS、LC-MS/MS)
LC2MS/MS方法可对含芬太尼及其它毒物成分的血浆同时检测分析,可大大节省分析时间,节约实验室资源,且与前述检测分析方法相比,具有更高的灵敏度,是近几年国内外检测血中芬太尼最常用的方法。Weng Naidong等应用LC2MS/MS检测人血浆中的多种毒物,芬太尼的最低检测血药浓度为0.05ng/ml[1];J.Day等应用LC-MS/MS检测人血浆中的芬太尼,最低检测血药浓度为0.05ng/ml[21 ] ;D.E.Koch 等使用LC-MS/MS法同时检测灵长类动物血浆中的芬太尼、去甲芬太尼,芬太尼的最低检测血药浓度为0.025ng/ml[10]。N.2H.Huyny等应用LC-MS/MS法检测人血浆中芬太尼,最低检测浓度0.02ng/ml[11]。
2展望
近10年国内外对血浆中芬太尼的检测多向以下几个方向发展:(1)检测限要求逐渐降低,检材用量逐渐减少,分析灵敏度逐渐提高。(2)常规仪器有其各自的缺点,难以满足现代毒物分析的要求,仪器联用分析技术是发展的必然趋势。(3)对血浆的前处理要求快捷、高效、省时。(4) 要求检测方法简便、快捷、准确,实验可重复性高,对实际应用具有较强的指导性。
随着芬太尼在我国市场应用的日趋广泛,由芬太尼引发的中毒事件及案件有增无减。国内外关于血浆中芬太尼的检测已做了大量的工作和努力,随着高科技分析仪器的不断应用和计算机技术的发展,国外已经能够检测纳克级以下的血浆芬太尼。但迄今为止,国内外文献对血浆中芬太尼的检测分析多应用于药物动力学、毒理等临床研究。根据我国公安司法工作的要求,建立一套符合我国仪器、设备、技术实际的血浆中芬太尼的检测方法,对芬太尼中毒事件和案件提供的检材进行分析鉴定,能够判明是否存在芬太尼及其与事件的关系,为澄清当事人在事件中是否负有法律责任提供依据,为相关案件提供侦破线索和犯罪证据,或者为司法调节提供科学依据。
参考文献:
[1 ]
Naidong W , Bu H , Chen Y2L , et al. Simultaneous de2
velopment of six LC2MS2MS methods for the determina2
tion of multiple analytes in human plasma [J ] . J Pharm
Biomed Anal , 2002 ,28 :111521126.
[2 ]
Kuhlman J J ,McCaulley R. Fentanyl Use ,Misuse ,and
Abuse :A Summary of 23 Postmortem Cases[J ] . Journal
of Analytical Toxicology , 2003 ,27 :4992504.
[3 ]
张燕婉,张毅,胡小琴. 反相离子对色谱法测定人血浆中
芬太尼浓度[J ] . 中国药学杂志, 1998 ,133 (5) :301.
[4 ]
李正翔,赵晴,董伟林. 高效液相色谱法测定人血浆中芬
太尼浓度[ J ] . 中国医院药学杂志, 2004 , 24 ( 10) :
6072609.
[5 ]
Kumar K,Ballantyne J A ,Baker A B. A sensitive assay
for the simultaneous measurement of alfentanil and fent2
anyl in plasama [ J ] . J Pharm Biomed Anal , 1996 , 14 :
6672673.
[ 6 ]
Szeitz A , Riggs K W , Harvey2Clark C. Sensitive and
selective for fentanyl using gas chromatography with
mass selective detection [ J ] . J Chromatogr B , 1996 ,
675 :33242.
[ 7 ]
Fryirsa B , A Woodhouse , Huang J L , et al. Determita2
tion of subnanogram concent rention of fentanyl in plasma
by gas chromatography2mass spect romet ry and compra2
sion with standard radioimmunoassay[J ] . J Chromatogr
B , 1997 ,688 : 79285.
[8 ]
Portier E J G, de Blok K, Butter J J , et al. Simultane2
ous determination of fentanyl and midazolam using high2
performance liquid chromatograghy with ult raviolet de2
tection[J ] . J Chromatogr B ,1999 ,723 :3132318.
[ 9 ]
Choi H S , Shin H2C , Khang G, et al. Quantitive analy2
sis of fentanyl in rat plasma by gas chromatography with
nit rogen2phosphorus detection [ J ] . J Chromatogr B ,
2001 ,765 :63269.
[ 10 ]
Koch D E , Isaza R , Capenter J W , et al. Simultaneous
ext raction and quantitation of fentanyl and norfentanyl
f rom primate plasma with LC/ MS detection [ J ] . J
Pharm Biomed Anal , 2004 ,34 : 5772584.
[ 11 ]
Huyny N2H ,Tyrefors N ,Ekman L , et al. Determinati2
om of fentanyl in human plasama and fentanyl and nor2
fentanyl in human urine using LC2MS/ MS[J ] . J Pharm
Biomed Anal , 2005 ,37 : 109521100.
[ 12 ]
Liu Y, Wu Y, Zhong J , et al. Capillary GC Determina2
tion of Fentanyl and Midazolam in Human Plasma [J ] .
Microchemical Journal , 1996 ,53 :1302136.
[13 ]
Dot sikas Y, Loukas Y L , Siafaka I. Determination of
umbilical cord and maternal plasma concent rations of
fentanyl by using novel spect rophotomet ric and chemi2
luminescence enzyme immunoassys [ J ] . Analytical
Chimica Acta , 2002 ,459 :1772185.
[14 ]
Kaferstein H , Sticht G. Camparision of nonradoactive
microtiter plate enzyme immunoassays for the sensitive
detection of fentanyl [J ] . Forensic Science Internation2
al , 2000 ,113 :3532357.
[15 ]
Egan T D , Sharma A S , Ashburn M A , et al. Deter2
mitation of fentanyl in plasma by radioimmunoassay
[J ] . Anesthesiology , 2000 ,92 :6652773.
[ 16 ]
Valverde C R , Mama K R , Kollias2Baker C , et al . De2
termitation of subnanogram concent ren of fentanyl in
plasma by standard radioimmunoassay [ J ] . Am J Vet
Res , 2000 ,61 :9312934.
[17 ]
Lee D D , Papich M G, Hardie E M. Determitation of
subnanogram fentanyl in plasma by gas chromatogra2
phy2mass spect romet ry and standard radioimmunoassay
[J ] . Am J Vet Res , 2000 ,61 : 6722677.
[18 ]
Woestenborghs R J H , Stanski D R , Scott J C ,et al .
Determinatiom of fentanyl in human plasama [J ] . An-
esthesiology , 1987 ,67 : 85.
[19 ]
Kowalski S R , Gourlay G K, Cherry D A ,et al. De2
terminatiom of fentanyl in human plasama by gas chro2
matography[J ] . J Pharm Methods , 1987 ,18 : 347.
[20 ]
Tsuchiya M , Ueda W , Tomoda M , et al. Determina2
tion of fentanyl using high2performance liquid chroma2
tograghy with ult raviolet detection[J ] . Jpn J Anesthesi2
ol , 1991 ,40 : 644.
[ 21 ]
Day J , Slawson M , Lugo R A , et al. Determinatiom of
fentanyl in human plasama using by gas chromatogra2
phy LC2MS/ MS [ J ] . J Anal Toxicol , 2003 , 27 :
5132516.