LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain Kits
实验概要
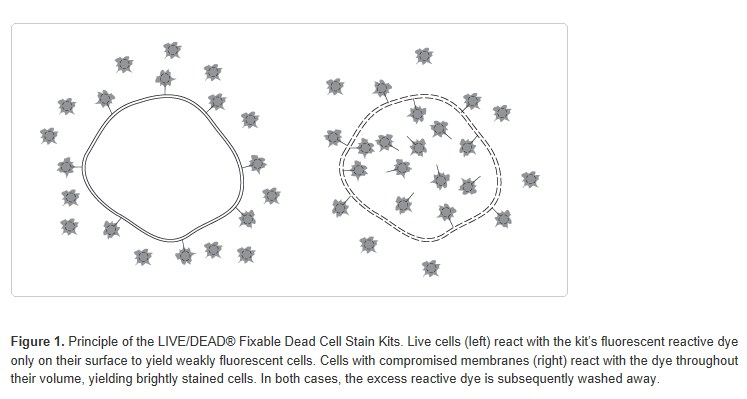
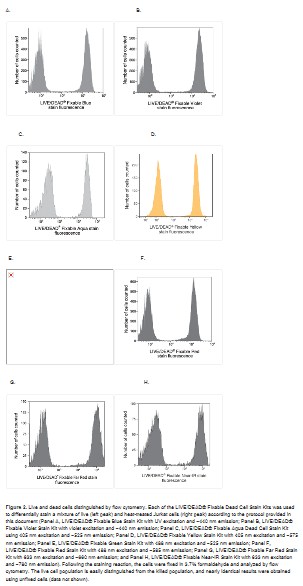
The LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain Kits use a novel method to evaluate the viability of mammalian cells by flow cytometry. These assays are based on the reaction of a fluorescent reactive dye with cellular amines. The reactive dye can permeate the compromised membranes of necrotic cells and react with free amines both in the interior and on the cell surface, resulting in intense fluorescent staining. In contrast, only the cell-surface amines of viable cells are available to react with the dye, resulting in relatively dim staining (Figure 1). The difference in intensity between the live and dead cell populations is typically greater than 50-fold (Figure 2). The discrimination is completely preserved following fixation of the sample by formaldehyde, under conditions that inactivate pathogens. Moreover, these single-color assays use only one channel of a flow cytometer, leaving the other channels available for multicolor experiments. The assays can also be used to detect dead cells by microscopy; however, the difference in fluorescence intensity of the live and dead cells can be appreciable, making it relatively difficult to simultaneously photograph the two populations.
The single-color LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain Kits are identical except for the fluorescent color of the included dye—blue, violet, aqua, yellow, green, red, far red, or near‑IR (infra red). Cells labeled by green fluorescent or red fluorescent reactive dye (L23101 and L23102, respectively) are excited by the 488 nm line of an argon-ion laser; green fluorescence is typically detected in the green channel of the flow cytometer (530/30 nm) and red fluorescence is detected in the red channel (630/30 nm). The blue fluorescent reactive dye (L23105) requires UV (350–360 nm) excitation with fluorescence emission read at ~450 nm. The violet fluorescent reactive dye (L34955) requires violet (~405 nm) excitation with fluorescence emission read at ~440 nm. The aqua fluorescent reactive dye (L34957) is efficiently excited with ~405 nm light (or UV light) and has fluorescence emission monitored at ~525 nm. The yellow fluorescent reactive dye (L34959) requires violet (~405 nm) excitation with fluorescence emission read at ~575 nm (appropriate channels for the violet-excitable reactive dyes may vary depending on the instrument). The far red (L10120) and near-IR (L10119) fluorescent reactive dyes are excited at 633/635 nm with fluorescence emission monitored at 665 nm and 775 nm, respectively.
The LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain Sampler Kit (L34960) contains one vial of each of the eight different fluorescent reactive dyes. Invitrogen also offers a LIVE/DEAD® Reduced Biohazard Cell Viability Kit (L7013) for determining cell viability. It is based on a different staining principle using two dyes of different colors, and is described separately.
Table 1. Approximate fluorescence excitation and emission maxima for the LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain single-color dyes.
Reactive dye | Excitation source | Ex* | Em* |
blue fluorescent reactive dye (L23105) | UV | 350 | 450 |
violet fluorescent reactive dye (L34955) | 405 nm | 416 | 451 |
aqua fluorescent reactive dye (L34957) | 405 nm | 367 | 526 |
yellow fluorescent reactive dye (L34959) | 405 nm | 400 | 575 |
green fluorescent reactive dye (L23101) | 488 nm | 495 | 520 |
red fluorescent reactive dye (L23102) | 488 nm | 595 | 615 |
far red fluorescent reactive dye (L10120) | 633/635 nm | 650 | 665 |
near-IR fluorescent reactive dye (L10119) | 633/635 nm | 750 | 775 |
*Approximate fluorescence excitation (Ex) and emission (Em) maxima, in nm.
主要试剂
Table 2. Contents and storage information.
Material | Amount | Storage | Stability |
Individual Kits: Blue, violet, aqua, yellow-, green, red,far red, or near-IR fluorescent reactive dye | 5 vials, each |
| When stored as directed, kit |
Sampler Kit: Blue, violet, aqua, yellow, green, | 1 vial of each dye |
| When stored as directed, kit |
Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), anhydrous (Component B | 500 μL |
| When stored as directed, kit |
Number of assays: Each individual kit provides sufficient material for approximately 200 flow cytometry assays, 40 assays per vial of the reactive dye. The Sampler Kit contains one vial of each fluorescent reactive dye with 40 assays per vial of the reactive dye, for a total of 320 assays per kit.
Approximate fluorescence excitation/emission maxima: See Table 2.
Before You Begin
Allow the reagents to warm to room temperature before opening the vials.
Materials Required but Not Provided
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS)
PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA)
Formaldehyde
AbC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit (if calculating compensation in multicolor immunophenotyping experiments using mouse antibodies)
ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit (if calculating compensation in multicolor experiments using a LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain)
Caution: DMSO is hazardous; avoid contact with skin and eyes and do not swallow. Handle reagents containing DMSO using equipment and practices appropriate for the hazards posed by such materials.
实验步骤
The following protocol has been used successfully in our laboratories to differentially stain live and dead cells and then to fix the cells in formaldehyde for subsequent analysis by flow cytometry. Excellent results have been obtained with a variety of cell types, including: Jurkat, MDCK, COLO205, CHO-K1, K-562, HeLa, P3X, 3T3, B35, BPAC, CHO-M1, A549, MMM, MRC5, U205, U266, 293 MSR, and RAW tissue-culture cell lines and human peripheral blood lymphocytes. If another staining reaction is to be performed on the same sample, determine the optimal staining sequence for the two procedures and whether or not the additional staining reaction will tolerate fixation by formaldehyde.
1. Dye Preparation
For convenience, the reactive dye in each individual kit is supplied in five separate vials, while the sampler kit contains one vial of each reactive dye. Each vial provides sufficient material for staining at least 40 cell samples. However, once reconstituted, the DMSO solution of reactive dye is somewhat unstable, especially if exposed to moisture. Unused portions may be used for up to 2 weeks if stored at ≤–20°C, protected from light and moisture.
1) Bring one vial of the fluorescent reactive dye (Component A) and the vial of anhydrous DMSO (Component B) to room temperature before removing the caps.
2) Add 50 μL of DMSO to the vial of reactive dye. Mix well and visually confirm that all of the dye has dissolved.
3) Use the solution of reactive dye as soon as possible (see below), ideally within a few hours of of reconstitution
2. Staining the Cells
Buffers appropriate for cell staining include phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), Hanks’ Balanced Salt Solution (HBSS), and Dulbecco’s PBS (D-PBS), without extraneous proteins such as bovine serum albumin or serum. When using an amino-reactive dye, for example the violet fluorescent reactive dye (Cat. no. L34955), Tris buffers and solutions containing sodium azide or extraneous protein should not be used for cell resuspension and washing.
1) Wash the cells once with 1 mL of PBS.
2) Resuspend the cells in 1 mL of PBS.
3) Count the cells and adjust the density with PBS to 1 × 106 cells in a 1 mL volume.
4) Add 1 μL of the reconstituted fluorescent reactive dye (from step 1.3) to 1 mL of the cell suspension and mix well.
5) Incubate at room temperature or on ice for 30 minutes, protected from light.
6) Wash the cells once with 1 mL of PBS, and resuspend the cells in 900 μL of PBS.
Note: If fixation is not required, then you can skip the steps 2.7–2.10 below. Instead, wash the cells twice with 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin, and resupend in 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin.
7) Add 100 μL of 37% formaldehyde.
8) Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes.
9) Wash once with 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin, and resuspend the cells in 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin.
10) Analyze the fixed cell suspension by flow cytometry using the appropriate excitation and detection channel (these may vary depending on instrument used):
Blue fluorescent reactive dye uses UV excitation and ~450 nm emission (450/50 nm or other filter)
Violet fluorescent reactive dye uses 405 nm excitation and ~450 nm emission (450/50 nm or other filter)
Aqua fluorescent reactive dye uses 405 nm excitation and ~525 nm emission (525/50 nm or other filter)
Yellow fluorescent reactive dye uses 405 nm excitation and ~575 nm emission (575/26 nm, 585/42 nm, or similar filter)
Green fluorescent reactive dye uses 488 nm excitation and ~530 nm emission (530/30 nm or other filter)
Red fluorescent reactive dye uses 488 nm excitation and ~ 585 nm emission (585/42 nm, 610/20 nm, or other filter)
Far red fluorescent reactive dye uses 633/635 nm excitation and ~660 nm emission
Near-IR fluorescent reactive dye uses 633/635 nm excitation and ~780 nm emission
3. Intracellular Staining
This procedure is completely compatible with common fixation and permeabilization methods for performing intracellular staining for flow cytometry. The procedure for staining with a LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain combined with immunophenotyping is as follows:
1) Centrifuge a sample of cells in suspension containing at least 1 × 106 cells. Discard the supernatant.
2) Wash the cells once with 1 mL of PBS.
3) Resuspend the cells in 1 mL of PBS.
4) Count the cells and adjust the density with PBS to 1 × 106 cells in a 1 mL volume.
5) Add 1 mL of the reconstituted fluorescent reactive dye (from step 1.3) to 1 mL of the cell suspension and mix well.
6) Incubate at room temperature or on ice for 30 minutes, protected from light.
7) Wash the cells with 1 mL of PBS and resuspend in 100 μl of PBS.
8) Stain as usual for surface markers, and incubate for desired time for antibody staining.
9) Wash the cells with PBS and resuspend in 900 μl of PBS
10) Add 100 μl of 37% formaldehyde.
11) Incubate at room temperature for 15 minutes.
12) Wash once with 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin, and resuspend the cells in 100 μl of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin.
13) Add permeabilization reagent and stain as usual for intracellular markers. Incubate for desired time for antibody staining.
14) Wash once with 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin, and resuspend the cells in 1 mL of PBS with 1% bovine serum albumin.
15) Analyze the fixed cell suspension by flow cytometry using the appropriate excitation and detection channel (from step 2.11)
4. Compensation Using ArC™ Amine Reactive Beads
The ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit is designed to facilitate compensation when using any of the LIVE/DEAD® fixable dead cell stains, providing a consistent, accurate and simple-to-use technique for the setting of flow cytometry compensation. The ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit includes two types of specially modified polystyrene microspheres to allow easy compensation of the LIVE/DEAD® fixable stains: the ArC™ reactive beads (Component A), which bind any of the amine-reactive dyes, and the ArC™ negative beads (Component B), which have no reactivity. After incubation with any amine reactive dye, the two kit components will provide distinct positive and negative populations of beads that can be used to set compensation. We recommend the following protocol for using ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit for compensation:
1) Gently vortex ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit components for 30 seconds to completely resuspend before use.
2) Add 1 drop of ArC™ reactive beads (Component A) to a labeled sample tube.
3) Allow ArC™ reactive beads to sit in the tube for 5 minutes to warm to room temperature.
4) Prepare fluorescent amine-reactive dye according to instructions included in the LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Kit. For optimal performance of the ArC™ reactive beads, use freshly prepared amine-reactive dye. Do not use previously frozen dye solution.
5) Add the amount of LIVE/DEAD® fixable dead cell stain listed in Table 3 to the bead suspension and mix well. Make sure to deposit the amine-reactive dye directly to the bead suspension.
Table 3. Amount of amine-reactive LIVE/DEAD® fixable dead cell stain for use with ArC™ reactive beads
Amine-reactive dye for use with | Amount |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Blue stain | 3 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Violet stain | 1 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Aqua stain | 3 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Yellow stain | 3 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Green stain | 3 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Red stain | 1 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Far Red stain | 3 μL |
LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Near-IR stain | 1 μL |
6) Incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature, protected from light.
7) Add 3 mL of PBS or other buffer to sample tube. Centrifuge for 5 minutes at 300 × g.
8) Carefully remove all the supernatant from tube. If using the red fluorescent reactive dye (Cat. no. L23102), repeat step 4.7.
9) Resuspend bead pellet by adding 0.5 mL of buffer to sample tube
10) Add one drop of ArC™ negative beads (Component B) to sample tube. Mix thoroughly.
11) Vortex tubes before analyzing using flow cytometry.
12) Perform manual or automatic compensation according to the preferred procedure for the flow cytometer in use. Gate on the bead singlet population based on FSC and SSC characteristics.
5. Combining ArC™ and AbC™ Kits
The AbC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit provides a consistent, accurate, and simple-to-use technique for the setting of flow cytometry compensation when using fluorochrome-conjugated mouse antibodies. The kit contains two types of specially modified polystyrene microspheres: the AbC™ capture beads (Component A) that bind all isotypes of mouse immunoglobulin, and the negative beads (Component B) that have no antibody binding capacity. After incubating with a fluorochrome-conjugated mouse antibody, the two components provide distinct positive and negative populations of beads that you can use to set compensation. You can use the AbC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit and the ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit together to calculate compensation in multicolor immunophenotyping experiments that incorporate a LIVE/DEAD® fixable dye by following the protocol outlined below:
1) Gently vortex the ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit and the AbC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit components for 30 seconds to completely resuspend before use.
2) Label a sample tube for the amine-reactive dye you are using and add 1 drop of ArC™ reactive beads (Component A in the ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit) to the labeled sample tube. Allow ArC™ reactive beads to sit in the tube for 5 minutes to warm to room temperature.
3) Prepare fluorescent reactive dye according to kit instructions included in the LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Dead Cell Stain Kit. For optimal performance of ArC™ reactive beads, always use freshly prepared amine-reactive dye. Do not use previously frozen dye solution
4) Add the amount of LIVE/DEAD® fixable dead cell stain listed in Table 3 to the bead suspension and mix well. Make sure to deposit the amine-reactive dye directly to the bead suspension.
5) Label another sample tube for each fluorochrome-conjugated antibody you are using, and add 1 drop of AbC™ capture beads (Component A in the AbC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit) to each labeled tube.
6) Add a pre-titrated amount of antibody conjugate to the appropriate tube and mix well. Make sure to deposit the antibody directly to the bead suspension
7) Incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature, protected from light
8) Add 3 mL of PBS or other buffer to each sample tube. Centrifuge at 300 × g for 5 minutes to collect beads.
9) Carefully remove all supernatant from each tube. If using the red fluorescent reactive dye (Cat. no. L23102), repeat step 5.8 for that tube.
10) Resuspend bead pellet by adding 0.5 mL of staining buffer to each sample tube.
11) Add one drop of negative beads (Component B in the AbC™ Anti-Mouse Bead Kit) to sample tube(s) containing the AbC™ capture beads.
12) Add one drop of ArC™ negative beads (Component B in the ArC™ Amine Reactive Compensation Bead Kit) to sample tube(s) containing the ArC™ reactive beads.
13) Vortex tubes before analyzing using flow cytometry.
14) Perform manual or automatic compensation according to the preferred procedure for the flow cytometer in use. Gate on the bead singlet population based on FSC and SSC characteristics.
附 件 (共2个附件,占88KB)
![]()
1.jpg
49KB 查看![]()
2.jpg
39KB 查看
-
项目成果

-
焦点事件

-
科技前沿

-
焦点事件