ELISA Protocol (General Guidelines)
实验概要
Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) involve attachment of a capture antibody to a solid phase support. Samples containing known or unknown antigen are then added in a matrix or buffer that will minimize attachment to the solid phase. An enzyme-labeled antibody is then added for detection.
The ELISA method is a benchmark for quantitation of pathological antigens and there are indeed many variations to this method. ELISAs are adaptable to high-throughput screening because results are rapid, consistent and relatively easy to analyze. The best results have been obtained with the sandwich format, utilizing highly purified, prematched capture and detector antibodies. The resulting signal provides data which is very sensitive and highly specific. Thus, Invitrogen offers a large menu of sandwich ELISA and phosphoELISA™ kits. ELISA and phosphoELISA™ kits allow for quantitative measurements of proteins outside and inside the cell, respectively. For intracellular proteins for signaling studies, we offer phosphoELISA™ kits for measurement of total and phosphorylation, modification, or cleavage site–specific proteins.
The phosphoELISA™ kit protocol (Figure 1) begins with a monoclonal antibody specific for a protein of interest (regardless of phosphorylation state) coated onto the wells of microtiter strips. Samples, including a standard containing protein of interest, control specimens, and unknowns, are pipetted into these wells. During the first incubation, the protein antigen binds to the immobilized (capture) antibody, much like an immunoprecipitation. After washing, a rabbit antibody specific for total protein or protein phosphorylated at a specific residue (e.g., Akt [pS473]) is added to the wells. During the second incubation, this antibody serves as a detection antibody by binding to the immobilized protein captured during the first incubation. After removal of excess detection antibody, a horseradish peroxidase–labeled anti–rabbit IgG antibody (anti-rabbit IgG-HRP) is added. This binds to the detection antibody to complete the four-member sandwich. After a third incubation and washing to remove all the excess anti-rabbit IgG-HRP, a substrate solution is added, which is acted upon by the bound enzyme to produce color. The intensity of this colored product is directly proportional to the concentration of total or phosphorylated protein present in the original specimen. Invitrogen® phosphoELISA™ kits have been designed to enable the specific detection of phosphorylation of key signaling molecules, offer great specificity, and correlate well to western blot data.
The assay procedure for ELISA (Figure 2) and phosphoELISA™ kits are similar with only a few minor differences. While the detector antibody for ELISA kits is biotin-labeled and is followed by incubation with streptavidin- HRP, the detector antibody for phosphoELISA™ kits is a rabbit polyclonal antibody and is followed by incubation with anti-rabbit IgG-HRP.
实验材料
1. ELISA Kit Contents
1) Calibrated standard
2) Stabilized chromogen
3) Antibody-coated 96-well plate
4) Stop Solution
5) Biotin-labeled detection antibody
6) Wash and Diluent buffers
7) Streptavidin-conjugated HRP
2. phosphoELISA™ Kit Contents
1) Calibrated standard
2) Stabilized chromogen
3) Antibody-coated 96-well strip-well plate
4) Stop Solution
5) Detection antibody
6) Wash and Diluent buffers
7) Anti-rabbit IgG-conjugated HRP
3. Materials Required But Not Included in the Kit
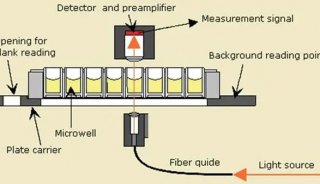
1) Absorbance-based Microplate Reader
2) Sample (See ELISA Sample Preparation Protocols)
The assay procedure takes about 4 hours total and requires only 30 minutes hands-on time. Allow all reagents to reach room temperature before use. Gently mix all liquid reagents prior to use.
Note: A standard curve must be run with each assay for quantification.
实验步骤
1. Determine the number of 8-well strips needed for the assay. Insert these in the frame(s) for current use. (Re-bag and seal extra strips and frame. Store these in the refrigerator for future use.)
2. Pipette 100 µl of the Standard Diluent Buffer to the well(s) reserved for the standard blanks. Well(s) reserved for chromogen blank(s) should be left empty.
3. Pipette 100 µl of standards, controls, and diluted samples (typically >1:10 dilution for cell extract) to the appropriate microtiter wells. Tap gently on side of plate to thoroughly mix.
4. Cover wells with plate cover and incubate for 2 hours at room temperature.
5. Thoroughly aspirate or decant solution from wells and discard the liquid. Wash wells 4 times.
6. Pipette 100 µl Streptavidin-conjugated HRP (ELISA kits) or Biotin-conjugated Detection Antibody (phosphoELISA™) solution into each well except the chromogen blank(s). Tap gently on the side of the plate to mix.
7. Cover wells with plate cover and incubate for 1 hour at room temperature.
8. Thoroughly aspirate or decant solution from wells and discard the liquid. Wash wells 4 times.
9. Pipette 100 µl streptavidin-HRP (ELISA kits) or anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (phosphoELISA™ kits) solution to each well except the chromogen blank(s).
10. Cover wells with the plate cover and incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature.
11. Thoroughly aspirate or decant solution from wells and discard the liquid. Wash wells 4 times.
12. Pipette 100 µl of Stabilized Chromogen to each well. The liquid in the wells will begin to turn blue.
13. Incubate for 30 minutes at room temperature and in the dark. Note: Do not cover the plate with aluminum foil or metalized mylar. The incubation time for chromogen substrate is often determined by the microtiter plate reader used. Many plate readers have the capacity to record a maximum optical density (OD) of 3.0. The OD values should be monitored and the substrate reaction stopped before the OD of the positive wells exceed the limits of the instrument. The OD values at 450 nm can only be read after the Stop Solution has been added to each well. If using a reader that records only to 3.0 OD, stopping the assay after 20 to 25 minutes is suggested.
14. Pipette 100 µl of Stop Solution to each well. Tap gently on the side of the plate to mix. The solution in the wells should change from blue to yellow.
15. Read the absorbance of each well at 450 nm having blanked the plate reader against a chromogen blank composed of 100 µl each of Stabilized Chromogen and Stop Solution. Read the plate within 2 hours after adding the Stop Solution.
16. Plot the absorbance of the standards against the standard concentration. (Optimally, the background absorbance may be subtracted from all data points, including standards, unknowns and controls, prior to plotting.) Draw the best smooth curve through these points to construct the standard curve. If using curve fitting software, the four parameter algorithm provides the best curve fit.
17. Read the protein concentrations for unknown samples and controls from the standard curve plotted in step 16. Multiply value(s) obtained for sample(s) by the appropriate dilution factor to correct for the dilution with Standard Diluent Buffer. (Samples producing signals higher than the highest standard should be further diluted in Standard Diluent Buffer and reanalyzed, multiplying the concentration by the appropriate dilution factor.)

附 件 (共1个附件,占51KB)
![]()
20120411_13423
51KB 查看
-
项目成果

-
产品技术